First pilot project of the concept of a coordinated presence at sea
The EU foreign ministers decided today (25 January) to launch a pilot project for a Coordinated Maritime Presence (CMP) in the Gulf of Guinea. This is the first time that the EU has responded in this way to an acute threat to freedom of navigation. The pilot project is set to run for one year - a review is due to take place in January 2022.
The CMP mechanism is intended to promote international cooperation at sea by strengthening the coordination of naval and naval air forces operating in the sea area concerned. It applies to any sea area in the world that is designated by the Council of the EU as a maritime area of interest. As a coordination instrument, it is intended to facilitate the exchange of information and situation analyses between existing units of the EU member states and the coastal states. In contrast to an operation (or mission), there is no actual deployment of armed forces ('force generation'). A Maritime Area of Interest Coordination Cell (MAICC) to be set up within the EU military staff is to pool the information and enable a joint analysis.
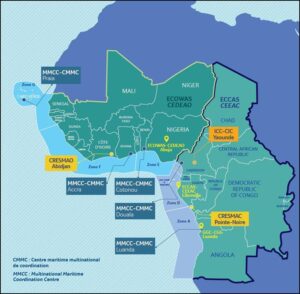
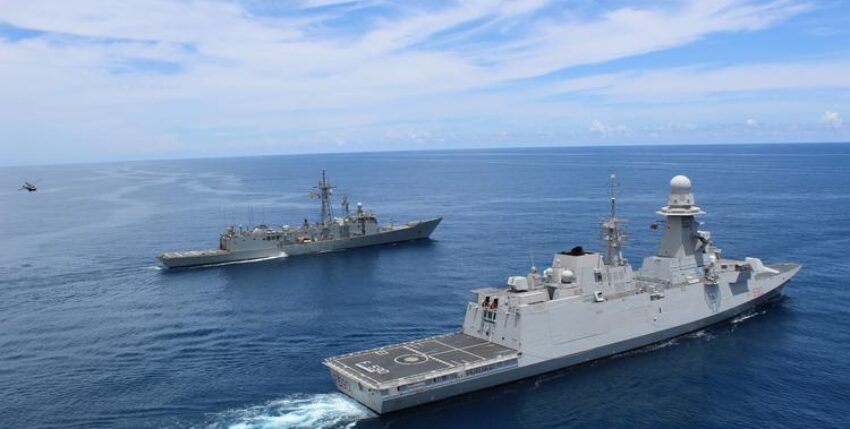
With the help of the mechanism, the EU wants to establish a permanent maritime presence in an area of special maritime interest. Below the threshold of an operation (or mission), synergy is to be created between the EU member states that are already present but operate independently of each other. In the case of the Gulf of Guinea, France, Italy and Spain are usually present with warships under national command. France has been running Operation Corymbe in the Gulf of Guinea since 1990. The deep-sea patrol vessel "Commandant Birot" (F 796) is currently on site. The 'Maritime Information Cooperation and Awareness Centre' (MICA Centre) in Brest processes the global information situation.
The Coordinated Maritime Presence (CMP) concept dates back to the informal meeting of defence ministers in Helsinki on 28-29 August 2019 and was adopted by the European Council on 17 June 2020.
The launch of the pilot project in the Gulf of Guinea supports the coastal states' initiatives under the Yaoundé architecture and reinforces the EU's efforts in the region. As part of its strategy for the Gulf of Guinea (2014) and a subsequently initiated action plan for the Gulf of Guinea, the EU already maintains a number of programmes and projects for experience and capacity building. The funds to be used for this come from both the Instrument for Security and Peace (IcSP) and the European Development Fund (EDF).
In its recently published annual report, IMB Piracy Reporting Centre (PRC) sees the situation in the Gulf of Guinea as a major driver of the increase in piracy cases in 2020 - 195 cases compared to 162 in 2019. Worldwide, 135 crew members were kidnapped from their ships in 2020. 95 per cent of them in the Gulf of Guinea (130 crew members) in 22 incidents. In addition, there were three ship hijackings in the region and nine additional cases of firearms being used on ships. Kidnappings of crew members were reported in 25 per cent of attacks on ships in the Gulf of Guinea - more than in any other region in the world.
Text: Hans-Uwe Mergener
Source: eeas.europa.eu
Photo: The EU launches its Coordinated Maritime Presences concept in the Gulf of Guinea - European External Action Service (europa.eu) (Photo)








